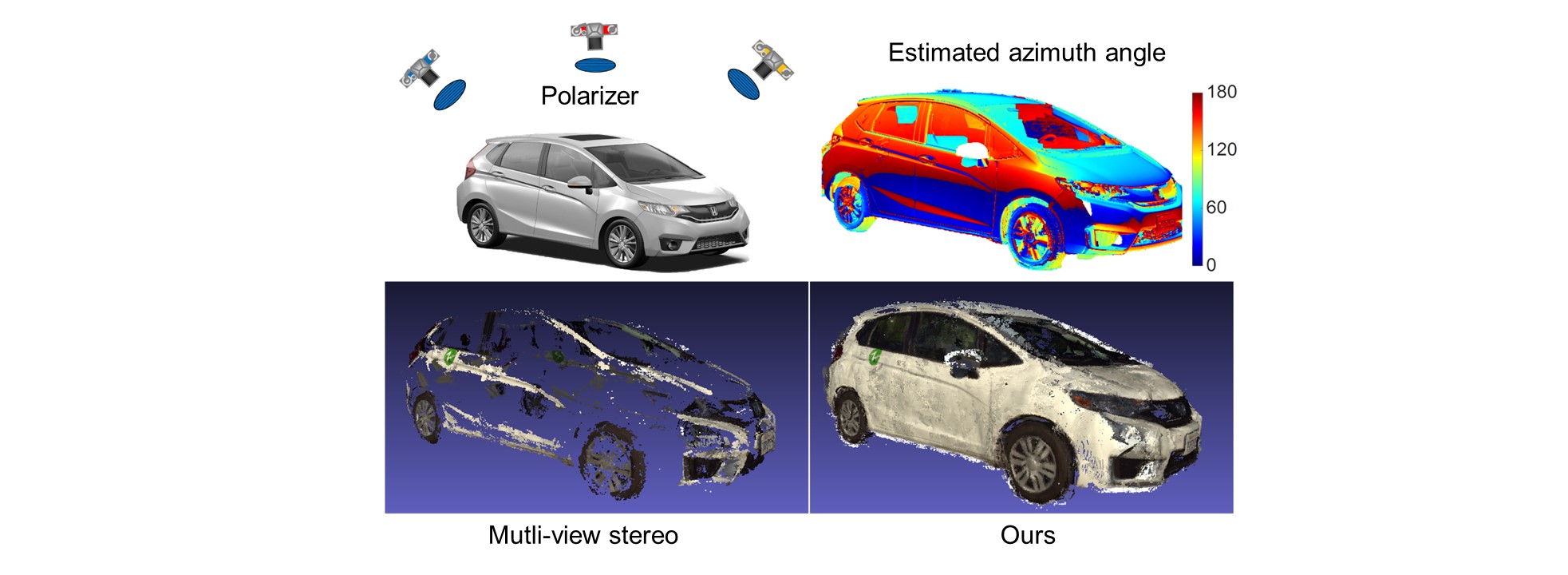
Multi-view stereo relies on feature correspondences for 3D reconstruction, and thus is fundamentally flawed in dealing with featureless scenes. In this paper, we propose polarimetric multi-view stereo, which combines per-pixel photometric information from polarization with epipolar constraints from multiple views for 3D reconstruction. Polarization reveals surface normal information, and is thus helpful to propagate depth to featureless regions. Polarimetric multi-view stereo is completely passive and can be applied outdoors in uncontrolled illumination, since the data capture can be done simply with either a polarizer or a polarization camera. Unlike previous work on shape-from-polarization which is limited to either diffuse polarization or specular polarization only, we propose a novel polarization imaging model that can handle real-world objects with mixed polarization. We prove there are exactly two types of ambiguities on estimating surface azimuth angles from polarization, and we resolve them with graph optimization and iso-depth contour tracing. This step significantly improves the initial depth map estimate, which are later fused together for complete 3D reconstruction. Extensive experimental results demonstrate high-quality 3D reconstruction and better performance than state-of-the-art multi-view stereo methods, especially on featureless 3D objects, such as ceramic tiles, office room with white walls, and highly reflective cars in the outdoors.
This study is partially supported by Nvidia, Canada NSERC Discovery Grant 31-611664, Discovery Accelerator Supplement 31-611663, and a project commissioned by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO).